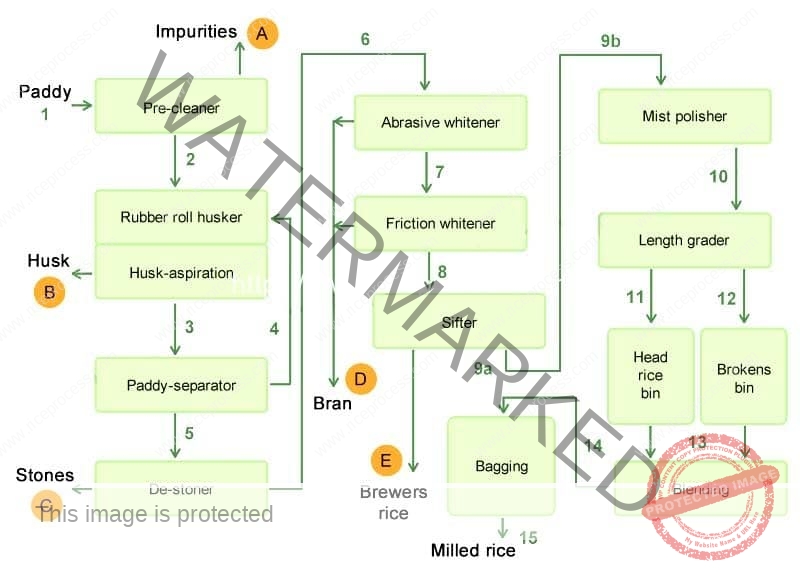
Introduction of Rice Mill Process Flow
Rice milling is the process that helps in removal of hulls and barns from paddy grains to produce polished rice. Rice forms the basic primary processed product obtained from paddy and this is further processed for obtaining various secondary and tertiary products. (Paddy in its raw form cannot be consumed by human beings. It needs to be suitably processed for obtaining rice.
Basic Rice Milling Processes Includes Following
Pre Cleaning: Paddy cleaner is the most essential equipment in a rice mill, as it separates all the impurities like dust, straw, sand, clay and heavy particles of even an uneven size from paddy. The advantages with the paddy cleaner are that it increases the life of rubber rollers and the percentage of oil in bran.
De-stoning: Separating stones from paddy.
Husking: This dehusking machine is used for the de-husking of paddy and removing of husk. The machine is based on the centrifugal principle.
Husk Aspiration: Separating the husk from brown rice and unhusked paddy.
Paddy Separation: Separating the unhusked paddy from brown rice.
Rice Whitening: Removing all or part of the bran layer and germ from brown rice. The rice whitener is used for whitening (i.e. removal of bran) of brown rice to white rice. Through a smooth flow of rice and an efficient aspiration system inside the machine,
the rice is whitened very gently.
Rice Polishing: Improving the appearance of milled rice by removing the remaining bran particles and by polishing the exterior of the milled kernel.
Rice Grading: Separating small and large brokers from head rice.
Blending: Mixing head rice with a predetermined amount of brokers, as required by the customer.
Weighing and bagging: Preparing the milled rice for transport to the customer.
Parboiling: Helps in improving the nutritional quality by gelatinization of starch inside the rice grain. It improves the milling recovery percent during deshelling and polishing, whitening operation..